Philadelphia's Influence on the Constitution's Creation
The Birthplace of American Democracy: Philadelphia
Philadelphia is often referred to as the birthplace of American democracy, and for good reason. It was here in 1776 that the Declaration of Independence was adopted, setting the stage for the nation’s future. This spirit of revolution and freedom laid a strong foundation for the later discussions that would lead to the Constitution.
Democracy is the government of the people, by the people, for the people.
The city became a gathering point for revolutionary thinkers, politicians, and everyday citizens who were passionate about shaping their government. The lively debates that occurred in Philadelphia helped to develop the ideas of liberty and justice that would permeate the Constitution. Think of Philadelphia as the fertile ground where the seeds of democracy were sown, nurtured by passionate voices.
As the birthplace of not just the Declaration but also the Constitution, Philadelphia's significance cannot be overstated. It was a melting pot of ideas, where various perspectives clashed and coalesced, ultimately leading to a framework that would guide the new nation for generations.
The Constitutional Convention: A Turning Point
In 1787, the Constitutional Convention convened in Philadelphia, marking a pivotal moment in American history. Delegates from twelve states (Rhode Island opted out) gathered to address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. This gathering was not just about drafting a new document; it was about redefining the very fabric of governance in the United States.
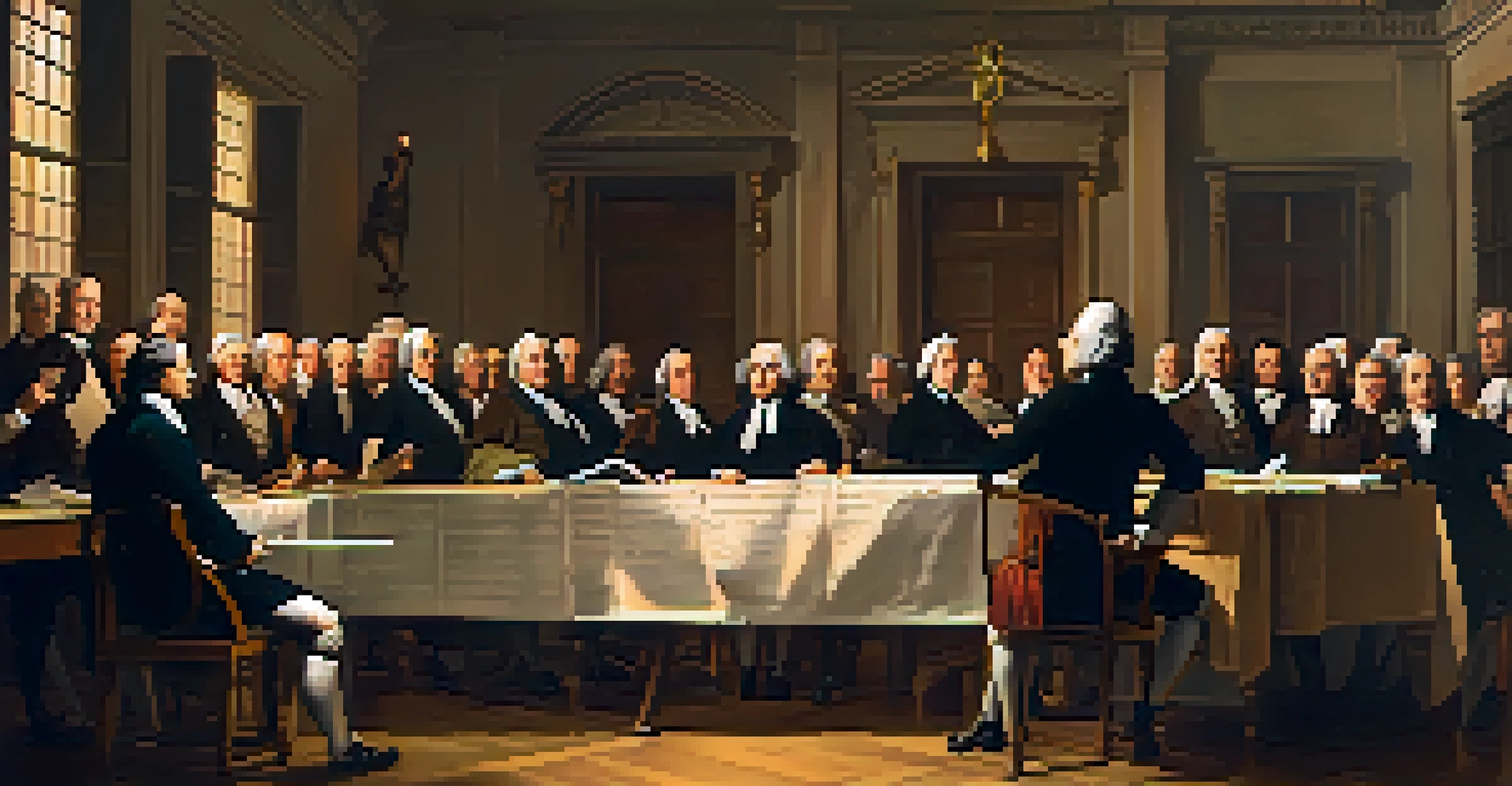

The debates were intense, with passionate arguments over representation, federalism, and individual rights. Imagine a room filled with some of the brightest minds of the time, each vying to ensure their vision of democracy was included in the new framework. It was a delicate dance of compromise and conviction, with each delegate needing to balance their state’s interests with the greater good of the nation.
Philadelphia: Democracy's Birthplace
Philadelphia was the site where the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution were crafted, establishing the foundation of American democracy.
Ultimately, the outcome of the convention was the U.S. Constitution, a document that established a government designed to endure. The debates and discussions that took place in Philadelphia not only shaped the Constitution itself but also set a precedent for future democratic processes.
Key Figures: The Architects of the Constitution
Several influential figures played crucial roles in the drafting of the Constitution, and many of them were based in or heavily associated with Philadelphia. George Washington, who presided over the convention, brought immense credibility and leadership to the proceedings. His presence ensured that the discussions remained focused and productive, much like a captain steering a ship through choppy waters.
The Constitution is not a mere piece of paper; it is the foundation of our democracy.
Other founding fathers, such as Benjamin Franklin and James Madison, were instrumental in shaping the Constitution’s content. Franklin’s wisdom and experience provided a sense of continuity, while Madison, known as the 'Father of the Constitution,' meticulously documented the debates and advocated for a strong central government. Together, these men, along with others, crafted a document that balanced power and liberty.
These key figures not only contributed their ideas but also engaged in the art of negotiation and compromise. Their collaborative efforts exemplified the importance of diverse perspectives in shaping a resilient framework for governance.
The Great Compromise: A Blueprint for Consensus
One of the most significant outcomes of the Constitutional Convention was the Great Compromise, which addressed the contentious issue of representation. Delegates from larger states wanted representation based on population, while smaller states sought equal representation. This conflict could have derailed the entire process, but through compromise, a bicameral legislature was born.
This compromise established the House of Representatives, with representation based on population, and the Senate, with equal representation for each state. It’s akin to a team sport where everyone gets a say, ensuring both larger and smaller players have a role in the game. This balanced approach helped to unify the states and laid the groundwork for future legislative processes.
The Great Compromise Achieved Unity
The Great Compromise created a bicameral legislature, balancing representation between large and small states, which was crucial for national unity.
The Great Compromise demonstrated that collaboration and negotiation could lead to effective solutions, which was a crucial lesson for the young nation. It set a precedent for how diverse interests could coexist within a single governing document, ultimately contributing to the Constitution's longevity.
The Bill of Rights: Protecting Individual Freedoms
While the Constitution established the framework of the government, the Bill of Rights was introduced to safeguard individual liberties. Ratified in 1791, these first ten amendments were a direct response to concerns that the original Constitution did not provide adequate protection for personal freedoms. It’s like having a safety net that ensures everyone can pursue their interests without fear of oppression.
The push for the Bill of Rights was largely championed by figures like James Madison, who acknowledged the need for explicit protections for citizens. The inclusion of rights such as freedom of speech, religion, and assembly became vital elements of American identity. These amendments were a crucial step in ensuring that the new government would remain accountable to its citizens.
The Bill of Rights continues to play a significant role in American law and culture, reminding citizens of their fundamental rights. This addition to the Constitution reflects Philadelphia’s lasting influence on the nation’s commitment to democracy and individual freedoms.
The Legacy of Philadelphia in Constitutional History
Philadelphia's impact on the Constitution extends far beyond its physical location; it represents a spirit of collaboration and compromise. The ideals discussed and debated within its walls have continued to shape American governance for over two centuries. This city has become a symbol of democratic ideals and the ongoing pursuit of a more perfect union.
The Constitution itself has been amended and interpreted over time, but the foundational principles established in Philadelphia remain intact. The city's role in this process showcases the importance of dialogue and adaptability in democracy. Just as Philadelphia evolved, so too has the Constitution, reflecting the changing values and needs of its people.
Bill of Rights Safeguards Freedoms
The Bill of Rights, ratified in 1791, was introduced to protect individual liberties and ensure government accountability to its citizens.
As we reflect on Philadelphia's influence, we recognize that the Constitution is more than just a document; it is a living testament to the spirit of its creators. The discussions that took place in this historic city continue to inspire generations, reminding us that democracy is a continuous journey, shaped by the voices of its citizens.
Visiting Philadelphia: A Journey Through History
For those intrigued by the role Philadelphia played in shaping the Constitution, a visit to the city offers a unique opportunity to step back in time. Sites like Independence Hall, where both the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution were debated and adopted, allow visitors to immerse themselves in history. Walking through these hallowed halls is like taking a journey through the very essence of American democracy.
The city boasts numerous museums and historical landmarks that provide context and insight into the founding principles of the nation. The National Constitution Center, for example, offers interactive exhibits that engage visitors with the Constitution's evolution and its relevance today. It’s an invitation to not just learn about history, but to appreciate how it continues to influence our lives.

Visiting Philadelphia is not just about witnessing history; it’s about connecting with the ideals that shaped a nation. As you explore this vibrant city, you can feel the echoes of those passionate discussions, making it a living testament to the power of ideas and the importance of civic engagement.